Staring at a dense, jargon-filled contract can feel overwhelming. The old-school approach—just reading from start to finish—is a recipe for missed details and unnecessary risk. A smarter workflow, however, starts with a solid framework that helps you work more efficiently, not just harder.
It all begins with a series of pre-checks and a strategic mindset before you even analyze a single clause. This initial phase transforms your review from a passive reading exercise into a proactive analysis, ensuring you catch critical errors right from the get-go.
The Power of Pre-Checks and Context
Before you dive into the complex legal language, do what the pros do: run some crucial preliminary checks. This isn't just about dotting i's and crossing t's; it's about verifying the absolute fundamentals of the agreement. Are the party names and addresses correct? Do the effective dates align with your project timeline? A simple typo in a company’s legal name can create huge enforcement headaches down the road.
Next, you need to understand the "why" behind the contract. What's the core business goal here? Knowing this context helps you evaluate whether the clauses actually support the intended outcome. For example, the restrictions in a software licensing agreement make a lot more sense when you know the business goal is to use it for internal purposes only, not for resale.
This simple, three-stage approach is the foundation of a modern initial review process.
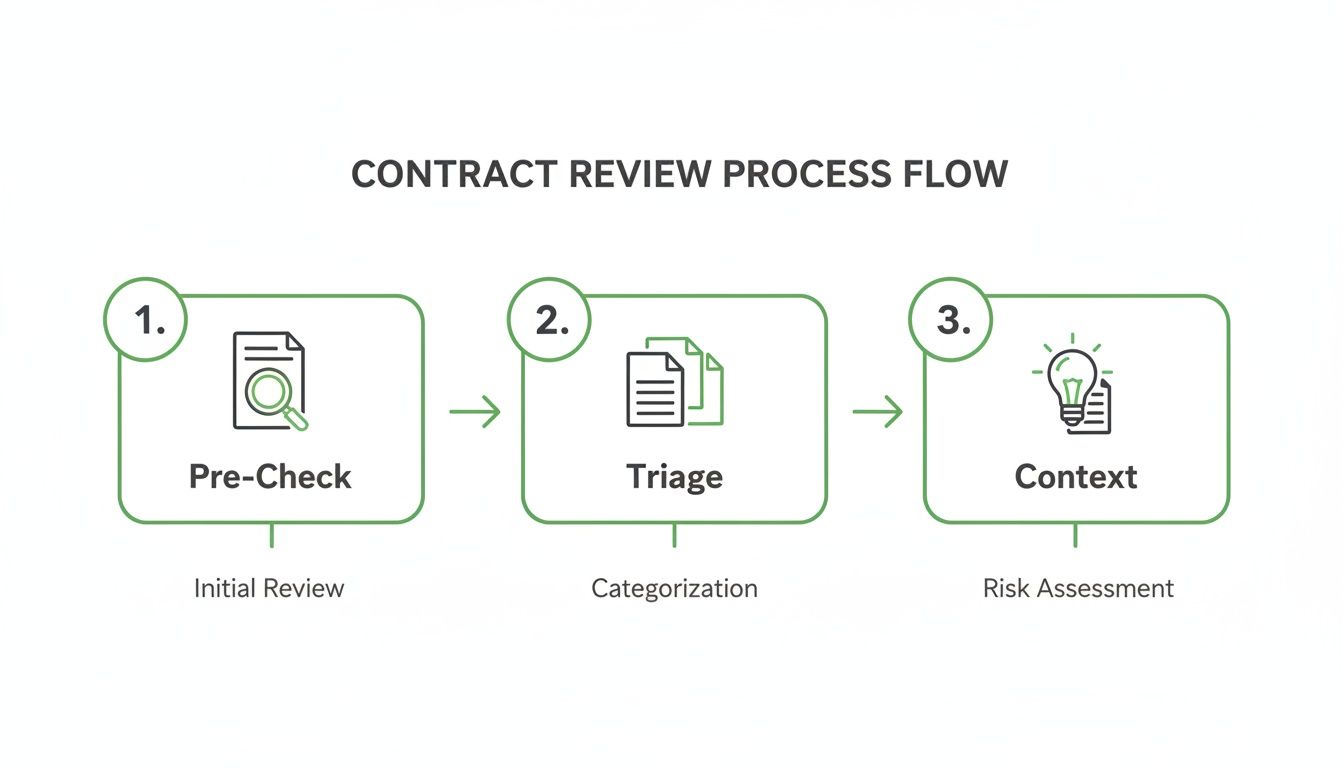
As the visual shows, a successful review starts by verifying the basic facts (Pre-Check), assessing its importance (Triage), and understanding the business purpose (Context).
Before digging into the dense clauses, use this quick reference to perform essential pre-review checks. It's a simple way to make sure the foundation of your agreement is solid.
Your Initial Contract Triage Checklist
| Check Area | What to Verify | Common Pitfall |
|---|---|---|
| Parties | Correct legal names, addresses, and entities. | Using a DBA or an incorrect subsidiary name. |
| Dates | Effective Date, Execution Date, and Term/Renewal dates. | Dates that don't align with project kickoff or deadlines. |
| Key Terms | Main deliverables, payment amounts, and timelines. | A mismatch between the deal memo and the contract language. |
| Attachments | All referenced exhibits, schedules, and addendums are included. | Missing an exhibit that contains critical details. |
| Signatories | The correct individuals are listed with proper titles. | A person without signing authority is listed. |
Running through this checklist first prevents you from wasting time on a document with fundamental flaws.
Categorize Contracts with a Triage System
Not all contracts are created equal. A standard non-disclosure agreement (NDA) for a quick chat is worlds apart from a multi-year master services agreement (MSA) worth millions. A triage system helps you categorize agreements so you can allocate your time and resources where they matter most.
You can create simple risk buckets:
- Low-Risk: Standard, template-based agreements with minimal financial or operational impact (e.g., event waivers, simple NDAs).
- Medium-Risk: Contracts involving moderate financial commitments or standard business processes (e.g., vendor agreements for non-critical services).
- High-Risk: Agreements with significant financial value, long-term commitments, intellectual property clauses, or substantial liability (e.g., major partnerships, enterprise software licenses).
This prevents you from spending three hours scrutinizing a low-risk contract while a high-risk deal sits waiting. This is especially vital when managing a high volume of documents, which is a core challenge addressed by many enterprise document management solutions.
The goal is to focus your deepest analysis where it counts the most. By triaging first, you ensure that high-stakes agreements get the meticulous attention they deserve, protecting your business from nasty surprises.
While this structured, manual process provides a solid foundation, technology is completely changing the game in terms of speed and accuracy. Industry studies show an average manual contract review takes about 92 minutes. In stark contrast, AI can perform a similar analysis in roughly 26 seconds, cutting manual labor by over 50% and improving accuracy. This frees you up to apply strategic thinking to what the technology flags, rather than spending hours just reading.
A Practical Guide to Critical Contract Clauses
Alright, you've done the basic checks and the contract's foundation seems solid. Now comes the real work: digging into the language that assigns risk, responsibility, and rights. This is where a contract review gets serious. We're going to skip the boilerplate definitions and jump straight to the clauses that can make or break a deal.
Understanding these sections isn't just a legal formality. It's about shielding your business from nasty surprises down the road. A single poorly worded sentence can quietly shift millions of dollars in liability from their side to yours.
The Heavy Hitters: Limitation of Liability and Indemnification
Let's start with the two most heavily negotiated clauses you'll ever see: Limitation of Liability (LoL) and Indemnification. Think of these as your financial safety nets.
The Limitation of Liability clause puts a hard cap on the maximum amount of money one party has to pay the other if things go sideways. Without it, your financial exposure is technically infinite. A fair and common approach is to cap the liability at the total amount paid under the contract over a specific period, like 12 months.
Indemnification is a different beast. It’s a promise from one party to cover the other's legal costs if a third party sues them over something related to the contract. For example, if a software vendor gives you a product that infringes on someone else's patent and you get sued, a good indemnification clause forces the vendor to pay your legal fees and any damages.
Key Takeaway: Never, ever accept a contract with unlimited liability. A reasonable Limitation of Liability clause is non-negotiable. Likewise, make sure the indemnification clause actually covers realistic risks like intellectual property infringement and data breaches.
Here are a few red flags to watch for:
- One-sided Indemnity: The clause only makes you responsible for covering their losses, with no reciprocity.
- Sneaky Carve-outs: The LoL clause has broad exceptions for things like "breach of confidentiality" or "data breach," which can make the liability cap completely worthless.
- Excluding Direct Damages: Look for tricky language that tries to exclude their liability for "direct damages"—the most basic and predictable losses from a breach.
Decoding Termination and Renewal Clauses
Getting out of a contract is just as important as getting into one. The Termination clause lays out the official exit strategies for both sides. A well-balanced agreement should always allow for "termination for cause" (if the other party messes up) and, ideally, a "termination for convenience."
Termination for convenience lets either party end the deal without having to prove a breach, usually by giving 30 or 60 days' notice. This gives you critical flexibility if your business needs suddenly change.
Right next to it, you'll often find an auto-renewal clause. This sneaky bit of language automatically extends the contract for another term unless you actively give notice to cancel. They're convenient, sure, but they can easily trap you in a deal you no longer want if you forget to mark your calendar.
A thorough contract review means scrutinizing every single obligation and deliverable before you sign.

This image is a great reminder to pause and carefully examine each section, making sure the terms truly align with your goals before you commit.
Confidentiality and Intellectual Property
Confidentiality clauses are there to protect any sensitive info you share. The main trap here is an overly broad definition of "Confidential Information." It shouldn't cover anything that's already public knowledge or that your team developed on its own. Also, check that the obligation has a reasonable time limit—often 3-5 years is fair, though trade secrets should be protected forever.
Intellectual Property (IP) clauses determine who owns what, which is mission-critical in any service agreement where something new is being created.
Key IP Questions to Answer
- Who Owns the Final Product? Does the contract state clearly that you own the work product you're paying for? This is usually handled with a "work for hire" or IP assignment clause.
- What About Their Pre-existing IP? The other party will almost always retain ownership of their underlying tools and tech. That's fine, but you need to make sure you get a broad, perpetual license to use any of their pre-existing IP that ends up in your final deliverable.
- Are They Using Your IP? If the clause grants them a license to use your company's IP, it must be strictly limited to what's needed to perform the services for you—and nothing more.
If you don't nail down clear IP ownership, you could end up paying for something you don't even own. This is where a detailed contract review saves you from massive headaches and legal battles later on.
Using Technology to Your Advantage
Relying on a manual contract review is a recipe for missed details and wasted hours. While your human judgment is irreplaceable for understanding business context and negotiation strategy, technology can handle the tedious, repetitive work that leads to burnout and errors. Smart tools don't replace your expertise—they amplify it.
Poor contracting practices can seriously eat into a company's bottom line, with recent data showing an average value loss of 8.6%. To fight this, 78% of organizations have invested in Contract Lifecycle Management (CLM) solutions, and 42% have upgraded their systems in just the last 12 months. The takeaway? Tech isn't just a "nice to have" anymore; it's a core part of modern contract management.
Instantly Spot Changes with AI Compare
One of the most nerve-wracking parts of any negotiation is tracking changes between versions. Did they only highlight the big edits, or did they sneak in a subtle change to a liability clause? Manually comparing two 20-page documents line-by-line is a high-stakes invitation for human error.
This is where a tool like PDFPenguin’s AI Compare becomes your best friend. Instead of a manual slog, you just upload both versions of the contract. The tool instantly highlights every single difference, from a deleted comma to a completely rephrased paragraph.

The side-by-side view gives you a clear, color-coded report of all additions and deletions. What used to take hours now takes minutes, giving you total confidence that you know exactly what’s been altered.
Securing and Organizing Your Contract Documents
A solid contract review process goes beyond just analysis—it includes managing the documents securely and efficiently. During negotiations, you might need to share versions with different people, but not everyone needs to see everything.
PDFPenguin gives you a suite of tools to handle these common situations:
- Redact Sensitive Data: Black out sensitive commercial terms or personal info before sending a contract to a third party. This protects confidentiality without creating a whole new document.
- Password Protect Files: Add a layer of security by password-protecting the PDF. This simple step ensures only authorized people can open the agreement.
- Merge and Split Documents: Negotiations often involve amendments, exhibits, and schedules. Merge everything into one organized PDF, or split a large contract to share just the pages you need.
Pro Tip: Create a simple file-naming system like "MSA_VendorX_v3_2024-10-26.pdf". This habit, combined with merging and splitting files, eliminates confusion and makes sure everyone is working from the correct document.
This is where having a toolbox of PDF utilities really shines. Instead of getting bogged down by administrative tasks, you can focus on the strategic parts of the review.
How PDFPenguin Solves Common Contract Headaches
| Tool/Feature | Common Pain Point Addressed | Practical Application |
|---|---|---|
| AI Compare | "Did I miss a small but critical change?" | Upload v1 and v2 of a contract. Instantly see every added or deleted word so you can focus your negotiation on what matters. |
| Redact PDF | "I need to share this with a consultant, but they can't see the pricing." | Permanently black out confidential financial details before sending the document for external review. |
| Password Protect | "This final draft can't be seen by anyone outside the deal team." | Secure the PDF with a password before emailing it to stakeholders, preventing unauthorized access. |
| Merge PDF | "I have the main agreement, three exhibits, and two schedules as separate files." | Combine all five documents into a single, easy-to-manage PDF for signing or final review. |
| Split PDF | "The finance team only needs to see the payment terms on pages 12-14." | Extract just those three pages from the main contract and send them as a separate, smaller PDF. |
These tools aren't just about convenience; they're about reducing risk and saving time that you can reinvest in higher-value work.
From Review to Summary
After the review is complete, you often need a high-level summary for stakeholders. Executives or project managers need to understand the key obligations and risks without reading the entire legal document.
Manually drafting these summaries is another time sink. After using tools to compare and finalize your document, you can use AI-powered features to get a first draft of the summary in seconds. If you're looking for ways to do this, you can learn more about how to summarize a PDF efficiently. This lets you produce accurate, concise overviews that get the whole team aligned on the contract’s core terms.
How to Handle Red Flags and Negotiate Better Terms
Spotting a problematic clause in a contract is a good start, but it's only half the job. The real work begins when you stop analyzing and start acting—turning a one-sided document into a fair agreement that actually protects you. This means knowing what to look for and having a solid plan to fix it.
Negotiation isn’t about picking a fight. It’s about proposing reasonable, business-focused solutions that build a balanced partnership. When you can explain why a clause is a problem and offer a fair alternative, you're not just editing a document—you're building a stronger business relationship from day one.
Common Red Flags and How to Address Them
Certain clauses should make you pause during any contract review. They often hide in plain sight but can pack a serious amount of risk. Let's break down a few of the usual suspects and what to do when you find them.
First up is the unilateral modification clause. This little gem gives the other party the power to change the terms of the deal whenever they want, often with just a quick email. It completely destroys the certainty you thought you had.
- Your Action: Propose language that requires both sides to agree on any changes. A simple edit can fix this. For example, change "Vendor may modify these terms at any time" to "Any amendments to this Agreement must be in writing and signed by both parties."
Another classic is the vague scope of work. When deliverables, timelines, and responsibilities are fuzzy, you're just asking for an argument later about what was actually promised. Ambiguity almost always benefits the party that doesn't have to do the work.
- Your Action: Insist on specifics. Use a detailed exhibit or even just bullet points to list out the exact deliverables, key performance indicators (KPIs), and deadlines. If it’s not written down, assume it won’t get done.
Finally, keep an eye out for the dreaded auto-renewal clause. This one automatically locks you into another term unless you send a cancellation notice by a very specific date. It's an easy way to get stuck paying for something you no longer want or need.
- Your Action: Ask for the clause to be removed entirely in favor of a proactive renewal conversation. If they won't budge, negotiate for a much longer notice window (like 60-90 days) and ask them to send you a reminder before that window closes.
Your Negotiation Playbook
Once you've flagged a problem, your approach is everything. Instead of just deleting a sentence you don't like, show up with a good reason and a constructive alternative.
Frame your requests around business logic, not just legalese. Explaining that a vague scope of work could lead to project delays and cost overruns is way more effective than just saying it's "unclear." This frames you as a practical partner, not a difficult roadblock.
Key Insight: The best negotiation tactic is to tie every requested change back to a core business principle like fairness, clarity, or mutual success. This elevates the conversation from a legal tug-of-war to a collaborative effort to build a solid agreement.
These skills are more critical than ever. A September 2025 survey found that rising global trade tensions have made contracting much trickier. A staggering 92% of firms reported adding new tariff-related clauses, and 73% said this made their contracts more complex. As a result, 49% of professionals felt overwhelmed by the number of agreements needing renegotiation. You can read the full research about these global trade impacts to get a better sense of the shifting landscape.
Preparing for Pushback and Finding Middle Ground
The other side probably has reasons for the language they included, so be ready for some pushback. The trick is to have your counterarguments prepared.
Example Scenario
Let’s say you're negotiating a software agreement and want to cap their "limitation of liability" at the amount you've paid them over the last 12 months.
- Their Position: "Our standard policy is a liability cap of $50,000, no matter what you pay us."
- Your Response: "We get the need for a cap, but a fixed number doesn't really scale with the value of our partnership. Tying the liability to the fees paid makes sure the risk is proportional to the business we're doing together. It’s a pretty standard and fair approach for a SaaS agreement."
If they still won't move, look for a compromise. Maybe you agree to a higher fixed cap if they agree to strengthen the indemnification clause. Negotiation is about finding a solution both parties can live with—not about winning every single point.
Finalizing the Deal and Managing Your Agreements
After all the back-and-forth, you’re finally at the finish line. This is where a small mistake can undo hours of hard work. Before anyone puts ink to paper (or a digital signature to a file), you need a rock-solid plan to lock everything down.
This isn’t just a formality. It’s about cementing the deal and making sure the agreement is easy to manage for months or years to come. Skipping these final steps can lead to version control nightmares or, even worse, disputes over what was actually agreed upon.
Creating the Definitive Version
Once everyone gives the final nod, the first thing to do is create a single, clean "execution version." That means accepting all the tracked changes and scrubbing the document of any leftover comments or redlines. The goal is a pristine final copy that shows the complete agreement—without any distracting negotiation history.
Before you send that clean version out, run it through a document comparison tool one last time against the final redlined draft. Think of it as your ultimate safety net. It confirms no accidental or sneaky changes slipped in during the cleanup and gives you total peace of mind.
A final, clean version is non-negotiable. It eliminates any ambiguity and serves as the single source of truth for everyone involved. Never, ever sign a document that still has tracked changes or comments floating around.
Implementing Smart Version Control
Disorganized files are the fast track to post-deal chaos. The easiest way to avoid this is with a simple but strict file-naming convention. A clear system means anyone on your team can instantly find the final, signed agreement without a headache.
Try a straightforward format that includes the important stuff:
- Document Type: State what it is (e.g., MSA, SOW, NDA).
- Counterparty Name: Name the other party.
- Status: Mark it as DRAFT, FINAL, or SIGNED.
- Date: Use a YYYY-MM-DD format so files sort chronologically.
For example, a final agreement might be named: MSA_VendorCorp_SIGNED_2024-11-15.pdf. This simple habit crushes the risk of someone accidentally referencing an old draft.
Secure Execution and Storage
With the final document ready, it's time to get it signed. Electronic signatures are the standard now—they're fast, efficient, and provide a secure, legally binding way to close the deal without the hassle of printing and scanning.
Once it's signed, don't just dump the file into a random folder. Store the fully executed agreement in a centralized, secure spot that’s easy for key stakeholders to access. This could be a dedicated folder on a secure cloud drive or a proper contract management system. For more tips on managing your final documents, our guide on how to edit PDF documents has some practical advice.
Finally, do your team a favor: pull out the most important information and create a one-page summary. Highlight key dates, obligations, renewal deadlines, and termination notice periods. Handing this abstract to your finance, operations, or project management teams ensures they know their responsibilities without having to read the entire legal document. It's the key to smooth sailing from day one.
Burning Questions on Contract Review
When you're staring down a dense contract, a few key questions always seem to pop up. Whether this is your first time or your hundredth, getting clear on these common sticking points can save you a world of hurt. Here are the answers I give most often.
How Long Should This Actually Take?
Honestly, there's no single answer. A simple, one-page NDA? You could probably knock that out in 30 minutes with a sharp eye. But a sprawling Master Services Agreement with multiple exhibits? That could easily eat up several hours, if not days, of careful reading. It all comes down to the document's length, complexity, and how much is at stake.
The real game-changer, though, is how you use your time. The old way of doing things—a purely manual review—takes over 90 minutes on average. Modern tools slash that. An AI can give you a first-pass analysis in seconds. The goal isn't just to be fast; it's to be smart. Let technology handle the tedious work so you can focus on the big-picture strategy and negotiating the terms that really matter.
What's the Single Biggest Mistake People Make?
Easy. They dive straight into the legal weeds without checking if the business deal is even right. It's so tempting to get bogged down in the indemnification clause while completely missing that the payment schedule or delivery dates are totally wrong.
Think about it: if the core commercial terms don't match the handshake deal, then the most brilliantly drafted legal protections are worthless. The very first thing you should do is ask yourself, "Does this paper actually reflect the agreement we made?" Get that right, and everything else you do will stand on a solid foundation.
Can I Do This Myself, or Do I Really Need a Lawyer?
This is a judgment call, and it’s all about risk. For low-stakes, routine agreements like a simple event waiver or a standard NDA from a reputable company, you can often handle it yourself. You know the business context better than anyone, and with a solid checklist, you can spot the most common issues.
But when the stakes get high, you call in a professional. That means any contract involving:
- Serious money
- Your intellectual property
- Major liability or uncapped risk
A smart approach is to do the first review yourself. You'll get a handle on the document, identify the business-side concerns, and be able to ask your lawyer much more specific, intelligent questions. That saves them time, which saves you money.
How Do I Keep Track of All These Changes?
Negotiations can get messy fast. A simple back-and-forth of emails and attachments can quickly lead to version-control chaos, and that's where critical mistakes happen.
The most dangerous assumption you can make is that the other side only changed what they told you they changed. Always, always verify it yourself.
First, get your file naming straight. Something like MSA_VendorName_V2_OurChanges_2024-11-15.pdf tells the whole story at a glance. Always insist on seeing a "redline" or "track changes" version. But don't just trust it. When you get a new draft, run it through a tool like PDFPenguin's AI Compare. It will catch every single modification—from a deleted comma to a rewritten paragraph—so nothing slips through the cracks.
Ready to make your contract review process faster, safer, and more accurate? The suite of tools from PDFPenguin gives you everything you need to compare versions, redact sensitive data, and manage your documents with ease. Explore our tools today!

